GeForce GTX 1650 review and test in 2022 – can we play on it?
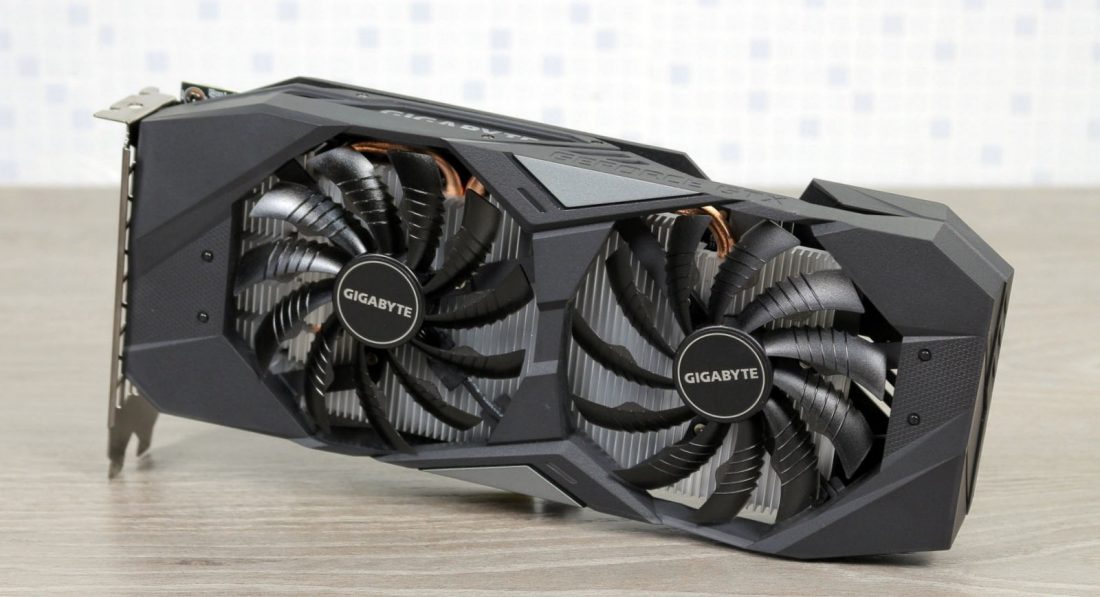
The GTX 1650 uses the new TU117 GPU, which is a smaller and therefore less expensive version of the TU116 that the GTX 1660 and 1660 Ti cards run on. Key differences from the 1660 series are memory configuration and the number of SM (stream multiprocessors), which in turn determines the number of CUDA cores, texture blocks and ROPs.
Characteristics
The novelty is built using 12nm TSMC, leaving 7nm for AMD Radeon VII. As a result, the chip size is about a third smaller than the TU116, with 4.7 billion transistors. The GTX 1650 has 4GB of GDDR5 memory, clocked at 8GT/s. Four active memory controllers on a 128-bit bus provide 128GB/s bandwidth.
It also features 32 ROPs (rendering pins). For the GPU core, the TU117 and GTX 1650 have 14 SM, meaning 896 CUDA cores and 56 texture blocks. Like all other Turing GPUs, the GTX 1650 can perform simultaneous FP32 and INT calculations, which can accelerate gaming workloads by 15-35% (depending on the game) compared to the previous Pascal architecture.
It’s worth noting that the desktop version of the 1650 doesn’t use the full TU117 either, as there is a mobile version with 16 SM and 1024 CUDA cores, so we could see a GTX 1650 Ti in the future. Nvidia tends to be conservative in claimed clock speeds, as most cards run well above the specified speed. “Standard” GTX 1650 is clocked at 1665MHz, giving a theoretical performance of 2984 GFLOPS.
The GTX 1650 is also designed to run without a 6-pin PCIe power connector, although factory overclocked cards (such as the MSI GTX 1650 Gaming X 4G) have higher clock speeds and require a 6-pin PEG connector.

Performance
Nvidia claims that the GTX 1650 will be twice as fast as the GTX 950, and 50% faster than the GTX 1050. That’s probably a fair estimate, especially as both of these cards only have 2GB of video memory. Given the specs, it should also be around 25-30% faster than the GTX 1050 Ti.
The performance boost is due to several changes. Firstly, the 1650 has more memory bandwidth and CUDA cores. Secondly, its clock speed is slightly higher. And third, the Turing architecture supports simultaneous FP32 and INT computation, which can improve performance by an additional 10-30% over Pascal GPUs.
Some details
The new Turing TU117 GPU that uses the GTX 1650 does not include the updated Turing NVENC block, but instead uses a version of Volta (which is basically the same as the Pascal version).
The Volta NVENC block isn’t bad, and it can probably handle any workload a gamer on a tight budget might face. Nevertheless, it’s still a step backwards, and it gives yet another reason to look at higher-end GPUs such as the GTX 1660 and above.